Understanding the First Great Civilization
Welcome to Mesopotamia—often called the “Cradle of Civilization.” This ancient land, nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, is where some of humanity’s most important milestones began. If you’ve ever been curious about the roots of cities, writing, and organized societies, this post is for you! Let’s explore what makes Mesopotamia so fascinating.
What is Mesopotamia?
The word “Mesopotamia” comes from Greek and means “land between rivers.” It lies in present-day Iraq and parts of Syria, Turkey, and Iran. This region is where early human societies first transitioned from hunting and gathering to settled farming. Over 5,000 years ago, Mesopotamia became home to groundbreaking developments that shaped our modern world.
Major Regions of Mesopotamia
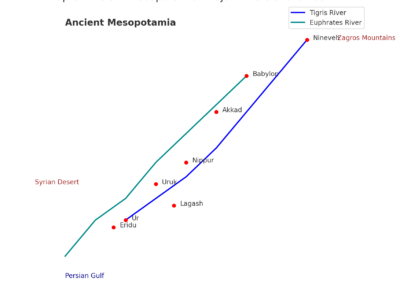
- Sumer: The southern part, known for inventing the earliest form of writing, cuneiform.
- Akkad: Famous for its powerful kings, including Sargon of Akkad, who established one of the world’s first empires.
- Babylonia: Known for the magnificent city of Babylon and its legendary king, Hammurabi, who created a famous code of laws.
- Assyria: Renowned for its fierce warriors and grand cities like Nineveh.
Why is Mesopotamia Called the Cradle of Civilization?
- Cities: Mesopotamians built some of the world’s first cities, like Uruk, Babylon, and Nineveh. These cities had bustling markets, towering ziggurats, and intricate systems of governance.
- Writing: The Sumerians of Mesopotamia invented cuneiform, one of the first writing systems, used to record everything from trade transactions to epic tales like The Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the earliest known works of fiction.
Fun fact: Early cuneiform tablets were basically ancient spreadsheets—proof that accounting has always been part of civilization! - The Wheel: Another groundbreaking invention was the wheel, first used for pottery and later adapted for transportation. Imagine how revolutionary it must have been to go from dragging things around to rolling them on carts!
- Laws: King Hammurabi of Babylon created one of the earliest and most comprehensive legal codes, known as the Code of Hammurabi. It covered everything from property rights to criminal justice and famously declared, “An eye for an eye.”
- Irrigation: To make the most of the Tigris and Euphrates, the Mesopotamians developed advanced irrigation systems. These systems allowed them to control water flow, turning deserts into productive farmland.
The Daily Life of Mesopotamians
Life in Mesopotamia revolved around agriculture, trade, and religion. Most people worked as farmers, artisans, or traders. The society was hierarchical, with kings and priests at the top, followed by scribes, merchants, and laborers.
Farming and Food
Mesopotamians grew crops like barley, wheat, and dates. They also raised livestock, including sheep, goats, and cattle. Beer was a staple drink, often brewed and consumed in large quantities.
Imagine a Mesopotamian farmer after a long day of work, relaxing with a clay mug of freshly brewed beer—talk about ancient happy hour!
Clothing and Fashion
People wore clothing made of wool or linen. Men typically wore tunics, while women wore long dresses. Jewelry was popular among both genders, with gold, silver, and lapis lazuli being prized materials.
Homes and Architecture
Homes were built from mud bricks, as stone and wood were scarce. Wealthier families had multi-room houses, while commoners lived in smaller, simpler homes. The grandest buildings were ziggurats, step-like temples dedicated to the gods.
Religion in Mesopotamia
Religion was central to Mesopotamian life. They worshipped a vast pantheon of gods, each responsible for different aspects of the world.
Major Deities
- Anu: God of the sky and the father of the gods.
- Enlil: God of air, storms, and kingship.
- Ishtar (Inanna): Goddess of love, war, and fertility.
- Shamash: God of the sun and justice.
Ziggurats were the focal point of worship. Priests played a significant role in society, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people.
Did You Know? Each city had its patron god or goddess, and their favor was believed to protect the people.
Entertainment and Leisure
Mesopotamians knew how to have fun, too! They played board games like the Royal Game of Ur, which involved strategy and luck. Music, dancing, and storytelling were also popular pastimes, especially during festivals.
Mesopotamian Achievements
- Mathematics: They developed the base-60 number system we still use to measure time.
- Astronomy: Mesopotamians tracked celestial movements and created early calendars.
- Literature: The Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the oldest known stories, comes from Mesopotamia and offers a glimpse into their values and beliefs.
Why Should You Learn About Mesopotamia?
Understanding Mesopotamia helps us appreciate how far humanity has come. From writing and urban planning to the concept of laws, this ancient civilization laid the foundation for much of what we enjoy today.
Explore More About Mesopotamia
If this beginner’s guide piqued your interest, stay tuned for more in-depth posts about Mesopotamian mythology, culture, and their incredible contributions to history. For a lighter, fun take on Mesopotamia, check out The Funny Epic of Gilgamesh, my humorous retelling of the legendary king’s adventures!